emailQ.NET - Anatomy of an Eml File
Instead of sending the message immediately, Smtp.NET
creates a file with a ".eml" file extension. Eml files contain
configuration name/value pairs
that are recognized by Microsoft IIS Smtp Server and emailQ.NET:
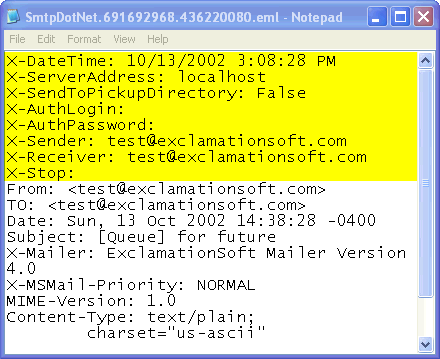
When Smtp.NET processes an Eml file, it reads the file and
determines how the message should be sent:
- X-ServerAddress: The name(s) of the SMTP mail server to send the message
through.
- X-SendToPickupDirectory: Specifies whether to send to the
pickup directory. Valid values are "True" and "False"
- X-PickupDirectory: (not shown) If X-SendToPickupDirectory is "True",
specifies the location of the Pickup Directory. This value overrides
the value stored in the system registry, which is configured in
Smtp.NET Manager.
- X-AuthLogin: Specifies the Authentication Login id to use when sending
the message. NOTE: if using Microsoft IIS Smtp Server, this value is
ignored.
- X-AuthPassword: Specifies the Authentication Login password to use when sending
the message. NOTE: if using Microsoft IIS Smtp Server, this value is
ignored.
- X-Sender: Specifies the sending email address. There is only one X-Sender
specified per Eml file
- X-Receiver: Specifies an email address to send the message to. There can
be multiple X-Receivers.
- X-Stop: Informs EmailQ.Net to stop reading the file.
Eml files can be modified or created manually by specifying the above configuration
name/value pairs. Omitting or incorrectly specifying configuration name/value will
cause EmailQ.Net to be unable to deliver the message. If messages cannot be
delivered, they are moved to the "Undeliverable" folder.
|